Cooling towers are not just towering structures dominating industrial landscapes; they are vital components of various industrial processes, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. These structures are commonly seen انواع برج خنک کننده to power plants, refineries, chemical plants, and other industrial facilities, but their significance often goes unnoticed by the general public. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of cooling towers, exploring their purpose, types, working principles, and environmental impact.
Purpose and Function
The primary function of a cooling tower is to dissipate excess heat generated during industrial processes, particularly those involving machinery or equipment that produce heat as a byproduct. The need for cooling arises in numerous industrial applications, such as power generation, manufacturing, and petrochemical refining. Without effective cooling mechanisms, equipment overheating can lead to reduced efficiency, equipment damage, and even catastrophic failures.
Types of Cooling Towers
Cooling towers come in various designs, each tailored to specific industrial requirements and environmental conditions. Broadly classified, cooling towers can be categorized into two main types:
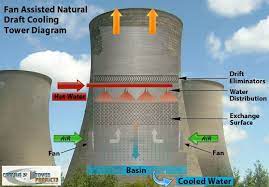
- Natural Draft Cooling Towers: These towering structures utilize the principle of natural convection to draw air through the tower. As warm air rises, it creates a pressure difference, pulling cool air from the surroundings into the tower. Natural draft cooling towers are typically large and are well-suited for applications requiring high cooling capacities, such as power plants.
- Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers: In contrast to natural draft towers, mechanical draft towers rely on mechanical fans to force air through the tower. This type of cooling tower offers more control over airflow and is commonly used in industries where precise temperature regulation is essential.
Additionally, cooling towers can be further classified based on their cooling method, such as evaporative cooling, dry cooling, or hybrid cooling, each offering distinct advantages depending on factors like water availability, environmental considerations, and efficiency requirements.
Working Principle
Regardless of their type, cooling towers operate on the principle of heat exchange through evaporation. Hot water or process fluid from industrial equipment is pumped into the cooling tower and distributed over a fill material, often made of plastic or wood, to maximize surface area. As this water flows over the fill material, it comes into contact with ambient air, facilitating heat transfer through evaporation. The heat absorbed by the water causes it to evaporate, thereby lowering its temperature. The cooled water is then collected at the bottom of the tower and recycled back into the industrial process, while the warm, moisture-laden air is released into the atmosphere.
Environmental Considerations
While cooling towers play a crucial role in industrial operations, they also raise environmental concerns, particularly regarding water usage and potential air pollution. Evaporative cooling towers consume significant amounts of water, leading to concerns about water scarcity, especially in arid regions or during periods of drought. Efforts to minimize water usage and enhance water conservation through technological advancements and improved operational practices are ongoing.
Additionally, cooling towers can emit pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and greenhouse gases, albeit in relatively small quantities compared to other industrial sources. Regulatory measures and technological innovations aim to mitigate these emissions and minimize the environmental impact of cooling tower operations.
Conclusion
Cooling towers are indispensable components of modern industrial infrastructure, ensuring efficient operation and longevity of equipment by dissipating excess heat. Their diverse designs and configurations cater to a wide range of industrial applications, from power generation to manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve and innovate, cooling towers will remain essential for maintaining operational efficiency while addressing environmental challenges through sustainable practices and technological advancements. Understanding the role and significance of cooling towers is crucial for fostering responsible industrial practices and sustainable development in the years to come.